Systematic workflow for model selection
Selecting the right embedding model involves navigating complex trade-offs between performance, cost, and operational requirements. A systematic workflow helps you make informed decisions based on your specific needs.
The complexity of model selection
Every embedding model involves trade-offs. The most obvious is the relationship between model performance, size, and cost:
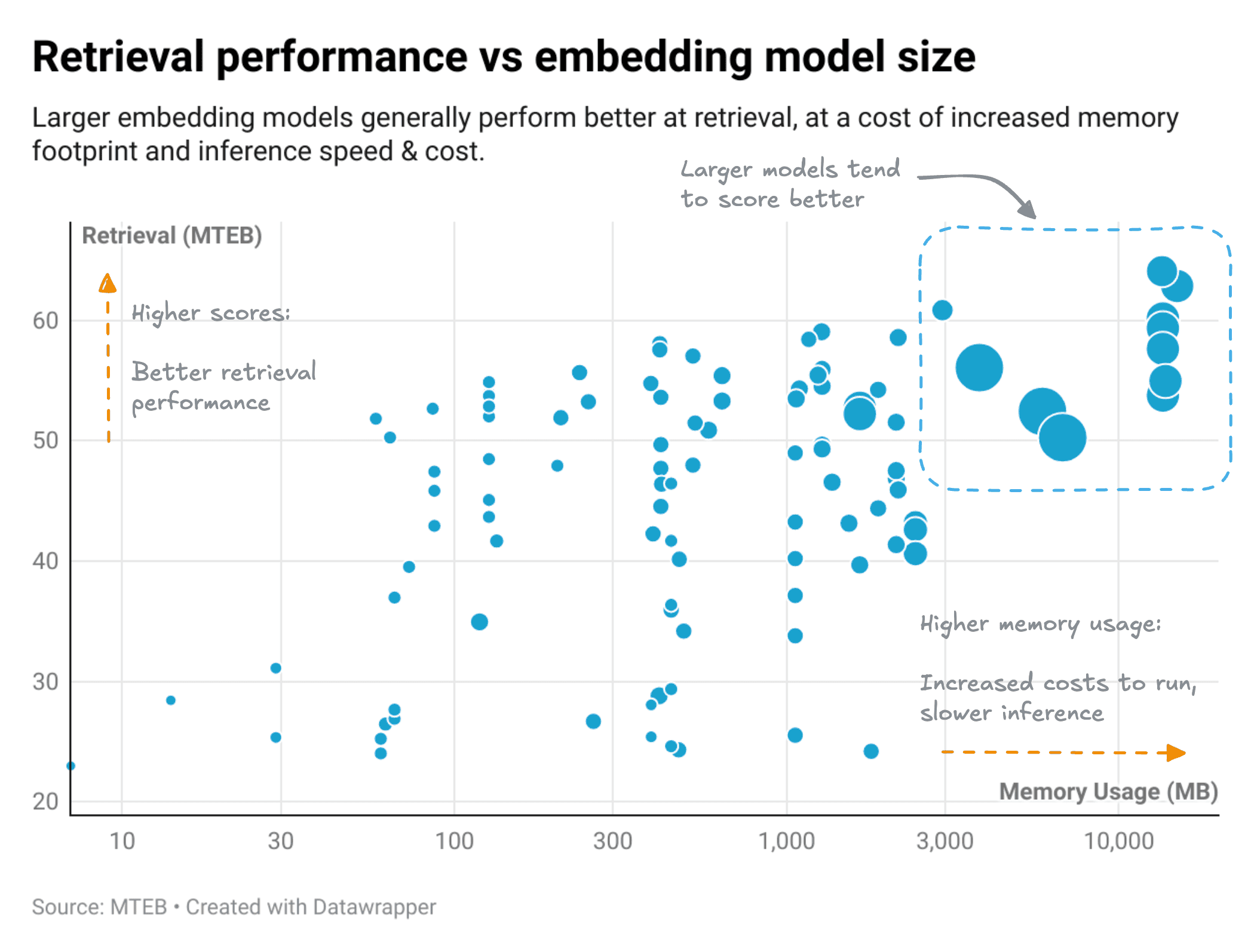
This chart shows a clear positive correlation between model size and retrieval performance. Generally:
- Larger models → Better performance → Higher costs and slower inference
- Smaller models → Adequate performance → Lower costs and faster inference
But size and performance aren't the only considerations. Other critical factors include:
- Deployment preferences: A proprietary model like Gemini may perform well but won't meet requirements for local inference
- Domain specificity: A model excelling at general benchmarks may underperform on specialized domains (legal, medical, coding)
- Operational complexity: Local models may be cheaper to run but require infrastructure expertise and maintenance
A systematic approach
To navigate this complexity effectively, we recommend a four-stage workflow:
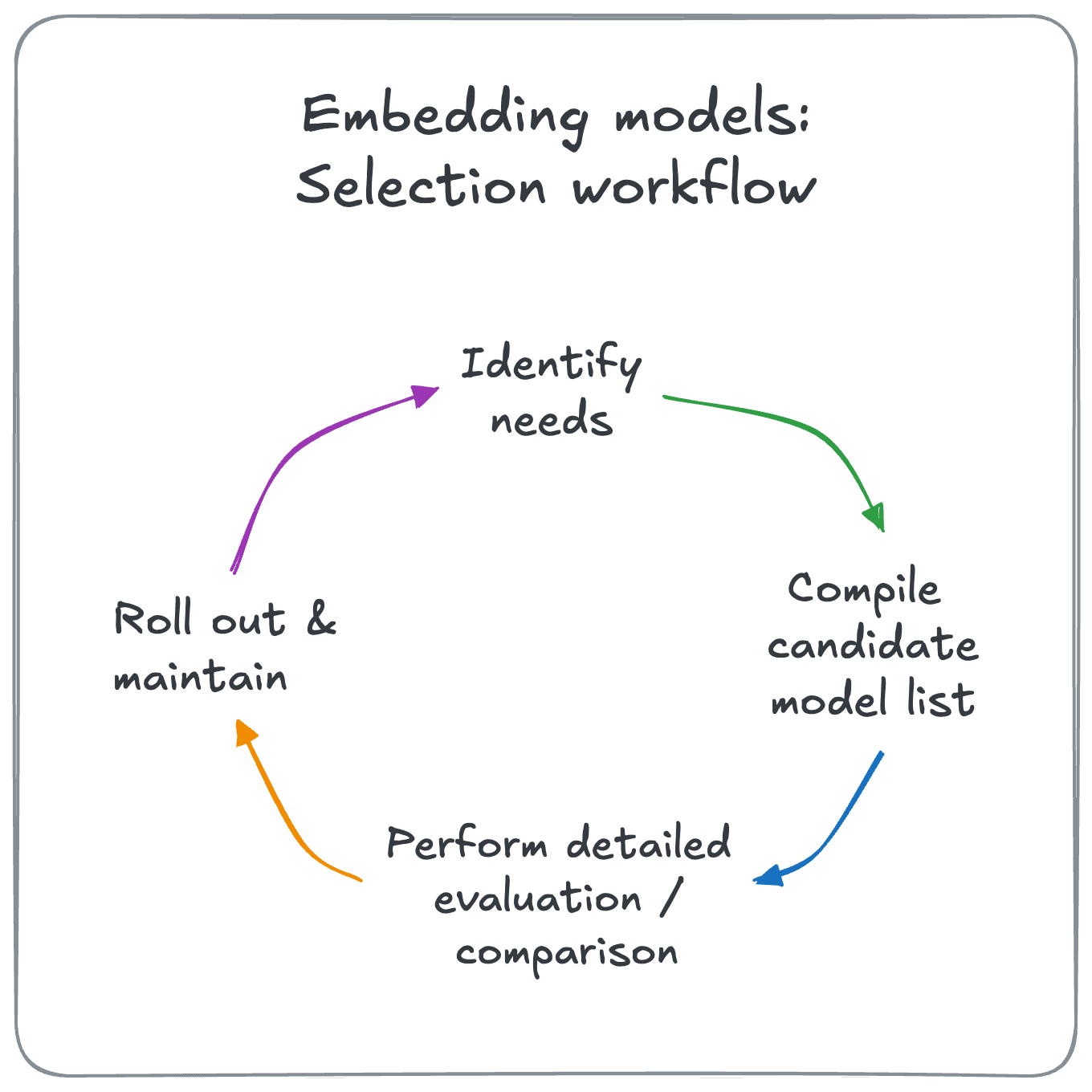
Stage 1: Identify your needs
Clearly articulate requirements and preferences across four key dimensions:
- Data characteristics (modality, language, domain, length)
- Performance needs (accuracy, latency, throughput, volume)
- Operational factors (hardware, deployment, maintenance)
- Business requirements (hosting, licensing, budget, compliance)
Stage 2: Compile candidate models
Create a manageable list of potentially suitable models using efficient screening heuristics:
- Filter by required modality support
- Prioritize models already available in your organization
- Include well-known, industry-standard models
- Consider benchmark leaders from MTEB and similar leaderboards
Stage 3: Detailed evaluation
Run comprehensive evaluations using your own data and use cases:
- Design evaluation criteria aligned with your requirements
- Create representative test datasets
- Measure performance on your specific tasks
- Compare results across candidate models
Stage 4: Periodic re-evaluation
Establish ongoing processes to reassess your model choice:
- Monitor changes in your data, application, or requirements
- Stay informed about new models and improvements
- Set regular review schedules
- Plan for model migration when beneficial
Why this workflow works
This approach balances thoroughness with efficiency:
- Systematic coverage: Ensures you consider all relevant factors
- Efficient screening: Avoids evaluating hundreds of models in detail
- Data-driven decisions: Uses your actual data and requirements, not just benchmarks
- Adaptive approach: Maintains relevance as your needs and the model landscape evolve
The workflow recognizes that there's no universally "best" embedding model – only the best model for your specific requirements and constraints.
Now that you understand the overall workflow, let's dive deeper into Stage 1: identifying your specific needs and requirements across all relevant dimensions.